Abstract
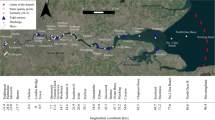
We have modeled the distribution of nine toxic metals in the surface sediments from 163 stations in the Venice lagoon using published data. Three entrances from the Adriatic Sea control the circulation in the lagoon and divide it into three basins. We assume, for purposes of modeling, that Porto Marghera at the head of the Industrial Zone area is the single source of toxic metals in the Venice lagoon. In a standing body of lagoon water, concentration of pollutants at distancex from the source (C 0) may be given byC=C 0e−kx wherek is the rate constant of dispersal. We calculatedk empirically using concentrations at the source, and those farthest from it, that is the end points of the lagoon. Averagek values (ppm/km) in the lagoon are: Zn 0.165, Cd 0.116, Hg 0.110, Cu 0.105, Co 0.072, Pb 0.058, Ni 0.008, Cr (0.011) and Fe (0.018 percent/km), and they have complex distributions. Given thek values, concentration at source (C 0), and the distancex of any point in the lagoon from the source, we have calculated the model concentrations of the nine metals at each sampling station. Tides, currents, floor morphology, additional sources, and continued dumping perturb model distributions causing anomalies (observed minus model concentrations). Positive anomalies are found near the source, where continued dumping perturbs initial boundary conditions, and in areas of sluggish circulation. Negative anomalies are found in areas with strong currents that may flush sediments out of the lagoon. We have thus identified areas in the lagoon where higher rate of sediment removal and exchange may lessen pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adami A, Cecconi G, and Degetto S (1992) Bathymetric survey and radiodating for evaluating the erosion of shallows (abstract). 23rd international conference on coastal engineering, Venice. pp 47–48
Avanzi C, Fossato V, Gatto P, Rabagliati R, Rosa Salva P, and Zitelli A (1981) Ripristino, conservazione ed uso dell'ecosistema lagunare Veneziano. Commune di Venezia, Italy. 199 pp
Barillari A (1978) Prime notizie sulla distribuzione dei sedimenti superficiali nel bacino centrale della Laguna di Venezia. Atti Ist Veneto Sci Let Arti 136:125–134
Barillari A (1981) Distribuzione dei sedimenti superficiali nel bacino meridionale della Laguna di Venezia. Atti Ist Veneto Sci Let Arti 139:87–109
Barillari A and Rosso A (1975) Prime notizie sulla distribuzione dei sedimenti superficiali della Laguna Veneta. Mem Biogeogr Adriatica Suppl 9:13–32
Barillari A, Boldrin A, Campesan G, and Rabitti S (1982) Relazione tra alcuni elementi in traccia e propieta' dei sedimenti in due aree campione della Laguna di Venezia. Ist Veneto Sci Let Arti Rapp Stud 8:87–103
Battiston GA, Degetto S, Gerbasi R, Sbrignadello G, and Tositti L (1988) The use of210Pb and137Cs in the study of sediment pollution in the Lagoon of Venice. Sci Total Environ 77:15–23
Bernardi S, Cecchi R, Costa F, Ghermandi G, and Vazzoler S (1986) Trasferimento di acqua dolce e di inquinanti nella Laguna di Venezia. Inquinamento, anno XXVIII, 1/2:2–20
Bogen J (1987) Deltaic depositional processes in a glacier-fed lake: A model for the fluvial/lacustrine interface.In: Ethridge FG, Flores RM, and Harvey MD (Eds), Recent developments in fluvial sedimentology, Tulsa, OK SEPM Sp. Pub. No. 39. pp 121–131
Bonham-Carter GF and Sutherland AJ (1968) Mathematical model and FORTRAN IV program for computer simulation of deltaic sediments. Computer Contribution No. 24, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, Kansas. 56 pp
Cavaleri L (1980) Sediment transport in shallow lagoons. Nuovo Cimento 3C 5:527–540
Cecchi R, Costa F, Ghermandi G, Vazzoler S, and Zonta R (1988) Caratterizzazione di un estuario in acque basse in Laguna di Venezia. Analisi granulometrica e di contenuto in metalli pesanti dei sedimenti superficiali. Associazione Italiana di Oceanologia e Limnologia, AIOL meeting, Pallanza. pp 283–292
Ciabatti M (1967) Ricerche sull'evoluzione del Delta Padano. G Geol 2, XXXIV, Fasc 2:26
Donazzolo R, Orio A, and Pavoni B (1982) Radiometrie dating and pollutants profiles in a sediment core from the Lagoon of Venice. Oceanol Acta 5 (no. Sp): 101–106
Donazzolo R, Orio A, Pavoni B, and Perin G (1984) Heavy metals in sediments of the Venice Lagoon. Oceanol Acta 7 (1):25–32
Donazzolo R, Calvo C, and Orio A (1988) Heavy metals in resuspended solid of the Venice Lagoon (abstract). Environmental contamination 3rd international conference, Venice. pp 350–353
Gatto P (1980) Il sottosuolo del littorale veneziano. CNR, Istituto Studio Dinamico Grandi Masse, Technical Report 108, Venezia
Gatto P and Carbognin L (1981) The lagoon of Venice: Natural environmental trend and man-induced modification. Hydrol Sci Bull 26 (4): 379–391
Gatto P and Previatello P (1974) Significato stratigrafico, comportamento meccanico e distribuzione nella Laguna di Venezia di un'argilla sovraconsolidata, nota come Caranto. CNR, Laboratorio per lo Studio della Dinamica delle Grandi Masse, Technical Report 70, Venezia
Ghermandi G, Cecchi R, Costa F, and Zonta R (1991) Trace metal distribution in aquatic systems studied by PIXE analysis of water and sediments. Nucl Instrum Phys Res B56/57:677–682
Ghetti A (1974) Problemi idraulici della Laguna di Venezia. Giornale Economico, Camera di Commercio di Venezia. pp 3–48
Hathaway JC, Buchholz ten Brink MR, Manheim FT, and Bothner MH (1994) Contaminated sediments in Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay: spatial and temporal trends (abstract). EOS, Trans Am Geophys Union 75 (3):144
Hieke Merlin O, Mcnegazzo Vitturi L, and Semewato G (1979) Contributo alla conoscenza dei sedimenti superficiali della Laguna Veneta. Atti Ist Veneto Sci Let Arti 137:35–51
Larsen B and Jensen A (1989) Evaluation of the sensitivity of the sediments stations in pollution monitoring. Mar Pollut Bull 20 (11): 556–560
Lehman JT (1975) Reconstructing the rate of accumulation of lake sediment: the effect of sediment focusing. Quat Res 5:541–550
Li Y-H (1991) Distribution pattern of the elements in the ocean: A synthesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:3223–3240
Mattiello G, Cecchinato C, Dell'Andrea E, Gambillara G, Goffo M. Marchiori M and Pasqualetto C (1988) Organic and inorganic contaminants in sediments of the Venice Lagoon (abstract). Environmental contamination 3rd international conference, Venice. pp 569–571
Menegazzo Vitturi L and Molinaroli E (1984) Il ruolo delle caratteristiche mineralogiche e fisiche dei sedimenti nei processi d'inquinamento in un'area tipo della Laguna Veneta. Ist Veneto Sci Let Arti Rapp Studi 9:353–367
Menegazzo Vitturi L, Molinaroli E, Pistolato M, and Rampazzo G (1989) Sediment properties and their influence on the geochemical composition in the lagoon of Venice. Boll Oceanogr Teor Appl 7:191–205
Molinaroli E and Rampazzo G (1986) Contributo alla conoscenza dei sedimenti superficiali della Laguna Veneta: Minerali pesanti. Atti Mem Accad Patavina Sci Lett Arti 97 (part II):159–176
Moore JN, Brook EJ, and Johns C (1989) Grain size partitioning of metals in contaminated coarse-grained river floodplain sediments: Clark Fork River, Montana U.S.A. Environ Geol Water Sci 14 (2):107–115
Pavoni B, Donazzolo R, Marcomini A, Degobbis D, and Orio A (1987) Historical development of the Venice Lagoon contamination as recorded in radiodated sediment cores. Mar Pollut Bull 18 (1):18–24
Rose S (1989) The heavy-metal adsorption characteristics of Hawthorne Formation (Florida, U.S.A.) sediments:Chem Geol 74:365–370
Scarponi G, Turetta C, Cecchini M, Novello D, Barbante C, Capodaglio G, and Cescon P (1993) Valutazione chemiometrica della qualita' di alcune componenti dell'ecosistema lagunare. Risultati di un'indagine pilota (abstract). Statchem 93 Statistica e chemiometria per lo studio dell'ambiente, Venezia. pp 15–29
Sfriso A, Marcomini A, and Pavoni B (1987) Relationships between macroalgal biomass and nutrient concentrations in a hypertrophic area of the Venice Lagoon. Mar Environ Res 22 (4):297–312
Simpson WR (1982) Particulate matter in the oceans—Sampling methods. Concentration, size distribution and particle dynamics. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 20:119–172
Tetzlaff DM and Harbaugh JW (1989) Simulating clastic sedimentation. New York:Van Nostrand, 202 pp
Yücesoy F and Ergin M (1992) Heavy-metal geochemistry of surface sediments from the southern Black Sea shelf and upper slope. Chem Geol 99:265–287
Zonta R, Costa F, Ghermandi G, Perin G, and Vazzoler S (1988) Pollution in estuarine areas at the Land-Venice Lagoon interface (abstract). Environmental contamination 3rd international conference, Venice. pp 557–560
Zonta R, Costa F, Ghermandi G, Pini R, Perin G, Traverso P, Vazzoler S, and Argese E (1992) Geochemical and chemical-physical characterization of a polluted mud flat in the Venice lagoon. Bull Inst Oceanogr Monaco 11:207–226
Zonta R, Zaggia L, and Argese E (1994) Heavy metals and grain-size distributions in estuarine shallow water sediments of the Cona marsh (Venice lagoon, Italy). Sci Total Environ (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basu, A., Molinaroli, E. Toxic metals in Venice lagoon sediments: model, observation, and possible removal. Geo 24, 203–216 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00766890
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00766890