Abstract
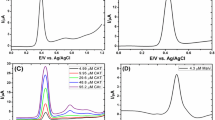
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-modified electrodes have been used for the estimation of the polyphenolic content and of the colour index of different samples of wines. Synthetic wine solutions, prepared with different amount of oenocyanins, have been analysed spectrophotometrically and electrochemically in order to find a correlation between the total polyphenolic content or colour index and the current peak. The regression curves obtained have been used as external calibration lines for the analysis of several commercial wines, ranging from white to dark red wines. In this way, a rapid estimation of the total polyphenolic content and of the colour index may be accomplished from a single voltammetric measurement. Furthermore, principal component analysis has also been used to evaluate the effect of total polyphenolic content and colour index on the whole voltammetric signals within a selected potential range, both for the synthetic solutions and for the commercial products.

Electrochemical sensors for the rapid determination of colour index and polyphenol content in wines







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bravo L. Polyphenols: chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr Rev. 1998;56:317–33.
Ross JA, Kasum CM. Dietary flavonoids: bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22:19–34.
Oliveira CM, Ferreira ACS, De Freitas V, Silva AMS. Oxidation mechanisms occurring in wines. Food Res Int. 2011;44:1115–26.
Gamella M, Campunzano S, Reviejo AJ, Pingarron JM. Electrochemical estimation of the polyphenol index in wines using a laccase biosensor. J Agric Food Chem. 2006;54:7960–7.
Garcia-Falcon MS, Perez-Lamela C, Martinez-Carballo E, Simal-Gandara J. Determination pf phenolic compounds in wines: influence of bottle storage of young red wines on their evolution. Food Chem. 2007;105:248–59.
Ainsworth EA, Gillespie KM. Estimation of total phenolic content and other oxidation substrates in plant tissues using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:875–7.
Jensen JS, Demiray S, Egebo M, Meyer AS. Prediction of wine color attributes from the phenolic profiles of red grapes (Vitis vinifera). J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:1105–15.
Sudraud P. Interpretation des courbes de’absorption des vin rouges. Ann Technol Agric. 1958;7:203–8.
Cimino F, Sulfaro V, Trombetta D, Saija A, Tomaino A. Radical-scavenging capacity of several Italian red wines. Food Chem. 2007;103:75–81.
Dell’Agli M, Buscialà A, Bosisio E. Vascular effects of wine polyphenols. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;63:593–602.
Merken HM, Beecher GR. Measurement of food flavonoids by high-performance liquid chromatography: a review. J Agric Food Chem. 2000;48:577–99.
Alonso ÁM, Guillén DA, Barroso CG, Puertas B, García A. Determination of antioxidant activity of wine byproducts and its correlation with polyphenolic content. J Agric Food Chem. 2002;50:5832–6.
Blasco AJ, Gonzalez Crevillen A, Gonzalez MC, Escarpa A. Direct electrochemical sensing and detection of natural antioxidants and antioxidant capacity in vitro systems. Electroanalysis. 2007;19:2275–86.
Turke A, Fischer W-J, Beaumont N, Kilmartin PA. Electrochemistry of sulfur dioxide, polyphenols and ascorbic acid at poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) modified electrodes. Electrochim Acta. 2012;60:184–92.
Makhotikina O, Kilmartin PA. The use of cyclic voltammetry for wine analysis: determination of polyphenols and free sulfur dioxide. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;668:155–65.
Kilmartin PA, Zou H, Waterhouse AL. Correlation of wine phenolic composition versus cyclic voltammetry response. Am J Enol Vitic. 2002;53:294–302.
da Silva LF, Stradiotto NR, Oliveira HP. Determination of caffeic acid in red wine by voltammetric method. Electroanalysis. 2008;20:1252–8.
Jakubec P, Bancirova M, Halouzka V, Lojek A, Ciz M, Denev P, et al. Electrochemical sensing of total antioxidant capacity and polyphenol content in wine samples using amperometry online-coupled with microdialysis. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:7836–43.
Šeruga M, Novak I, Jakobek L. Determination of polyphenols content and antioxidant activity of some red wines by differential pulse voltammetry, HPLC and spectrophotometric methods. Food Chem. 2011;124(3):1208–16.
Ziyatdinova G, Kozlova E, Budnikov H. Electropolymerized eugenol-MWNT-based electrode for voltammetric evaluation of wine antioxidant capacity. Electroanalysis. 2015;27:1660–8.
Curulli A, Di Carlo G, Ingo GM, Ricucci C, Zane D, Bianchini C. Chitosan stabilized gold nanoparticle-modified Au electrodes for the determination of polyphenol index in wines: a preliminary study. Electroanalysis. 2012;24:897–904.
Di Carlo G, Curulli A, Toro RG, Bianchini C, De Caro T, Padeletti G, et al. Green synthesis of gold-chitosan nanocomposites for caffeic acid sensing. Langmuir. 2012;28:5471–9.
Zikos N, Karaliota A, Liouni M. Chronoamperometry as a tool for the evaluation of antioxidant properties of red wines. J Anal Chem. 2011;66:859–64.
Ziyatdinova G, Kozlova E, Budnikov H. Chronocoulometry of wine on multi-walled carbon nanotube modified electrode: antioxidant capacity assay. Food Chem. 2016;196:405–10.
Legin A, Rudnitskaya A, Lvova L, Vlasov Y, Di Natale C, D’Amico A. Evaluation of Italian wine by the electronic tongue: recognition, quantitative analysis and correlation with human sensory perception. Anal Chim Acta. 2003;484:33–44.
Apetrei C, Apetrei IM, Villanueva S, de Saja JA, Gutierrez-Rosales F, Rodriguez-Mendez ML. Combination of an e-nose, an e-tongue and an e-eye for the characterisation of olive oils with different degree of bitterness. Anal Chim Acta. 2010;663:91–7.
Pigani L, Culetu A, Ulrici A, Foca G, Vignali M, Seeber R. Pedot modified electrodes in amperometric sensing for analysis of red wine samples. Food Chem. 2011;129:226–33.
Pigani L, Zanfrognini B, Seeber R. PEDOT-modified microelectrodes. Preparation, characterisation and analytical performances. Electroanalysis. 2012;24:1340–7.
Pigani L, Seeber R, Bedini A, Dalcanale E, Suman M. Adsorptive-stripping voltammetry at PEDOT-modified electrodes. Determination of Epicatechin. Food Anal Methods. 2014;7:754–60.
Bro R, Smilde AK. Principal component analysis. Anal Methods. 2014;6:2812–31.
Pigani L, Foca G, Ulrici A, Ionescu K, Martina V, Terzi F, et al. Classification of red wines by chemometric analysis of voltammetric signals from Pedot-modified electrodes. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;643:67–73.
Pigani L, Foca G, Ionescu K, Martina V, Ulrici A, Terzi F, et al. Amperometric sensors based on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-modified electrodes. Discrimination of white wines. Anal Chim Acta. 2008;614:213–22.
Savitzky A, Golay MJE. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal Chem. 1964;36:1627–39.
Aguirre MJ, Chen YY, Isaacs M, Matsuihir B, Mendoza L, Torres A. Electrochemical behavior and antioxidant capacity of anthocyanins from Chilean red wine, grape and raspberry. Food Chem. 2010;121:44–8.
Burn DT, Danzer K, Townshend A. Use of the terms recovery and apparent recovery in analytical procedures. Pure Appl Chem. 2002;74:2201–5.
Janeiro P, Oliveira Brett AM. Redox behavior of anthocyanins present in Vitis vinifera L. Electroanalysis. 2007;19:1779–86.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support for this research by University of Modena and Reggio Emilia through FAR 2014 and by Fondazione di Vignola through Ricerca Scientifica e Tecnologica-2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Chemical Sensing Systems with guest editors Maria Careri, Marco Giannetto, and Renato Seeber.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pigani, L., Rioli, C., Foca, G. et al. Determination of polyphenol content and colour index in wines through PEDOT-modified electrodes. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 7329–7338 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9643-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9643-4