Abstract
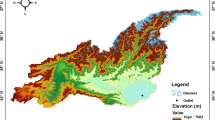
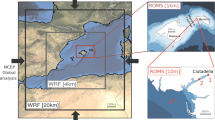
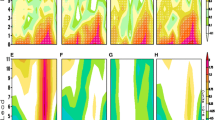
Climate change is likely to increase the pressure on the environment and on human systems that are requiring new assessment tools aimed at supporting decision-makers and stakeholders towards a more sustainable and effective management of the coastal environment and its resources. This research appraises an ensemble of models that integrates complex interactions of climate and anthropogenic impacts on vulnerable Mediterranean coastal areas with application to the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Starting from Global and Regional Circulation Models, the models’ ensemble includes simulations of marine and atmospheric dynamics and biogeochemical processes in coastal waters under expected anthropogenic forcings, with a spatial domain ranging from subnational to local. In the case study area, the simulations showed that atmospheric temperature increase is likely to be around 4 °C in the summer months of 2100, relative to 1961–1990. In order to obtain the most reliable estimate of sea-level rate variations, satellite altimetry data have been processed over a period of 15 years (1993–2007) showing that sea-level changes on the Tunisian shelf were of the order of 2 mm/year. This value was considered as a reference for the sea-level change scenarios. As far as the water quality is concerned, the areas most impacted by pollution are located near major towns and human infrastructures, such as harbours. The set of results obtained by the proposed models’ ensemble may be suitable for supporting a scientific dialogue with stakeholders and for the implementation of exposure scenarios supporting a regional risk assessment approach to the entire Gulf of Gabes area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adani M, Dobricic S, Pinardi N (2011) Quality assessment of a 1985–2007 Mediterranean Sea reanalysis. J Atmos Ocean Technol 28:569–589
Artebjerg G, Casartelli S, Dahl K, Hansen J, Nygaard K, Rygg B, Sorensen K, Severinsen G, Casartelli S, Schrimpf W, Schiller W, Druon NJ (2001) Eutrophication in Europe’s coastal waters (No. Topic Report 7). European Environmental Agency
Barhoumi S, Messaoudi I, Deli T, Saïd K, Kerkeni A (2009) Cadmium bioaccumulation in three benthic fish species, Salaria basilisca, Zosterisessor ophiocephalus and Solea vulgaris collected from the Gulf of Gabes in Tunisia. J Environ Sci 21:980–984
Baruffi F, Cisotto A, Cimolino A, Ferri M, Monego M, Norbiato D, Cappelletto M, Bisaglia M, Pretner A, Galli A, Scarinci A, Marsala V, Panelli C, Gualdi S, Bucchignani E, Torresan S, Pasini S, Critto A, Marcomini A (2012) Climate change impact assessment on Veneto and Friuli plain groundwater. Part I: an integrated modelling approach for hazard scenario construction. Sci Total Environ 440:154–166
Bel Hassen M, Hamza A, Drira Z, Zouari A, Akrout F, Messaoudi S, Aleya L, Ayadi H (2009) Phytoplankton-pigment signatures and their relationship to spring–summer stratification in the Gulf of Gabes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 83:296–306
Bonaduce A (2012) Sea-level climate variability in the Mediterranean Sea, PhD Thesis. University of Bologna
Bouwman AF, Kram T, Klein Goldewijk K (2006) Integrated modeling of global environmental change. An overview of IMAGE 2.4 (No. 500110002/2006). Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency, Bilthoven
Brohan P, Kennedy JJ, Harris I, Tett SFB, Jones PD (2006) Uncertainty estimates in regional and global observed temperature changes: a new dataset from 1850. J Geophys Res 111. doi:10.1029/2005JD006548:D12
Calafat FM, Gomis D (2009) Reconstruction of Mediterranean sea level fields for the period 1945–2000. Glob Planet Chang 66:225–234
Cazenave A, Llovel W (2010) Contemporary sea level rise. Annu Rev Mar Sci 2:145–173
Cazenave A, Cabanes C, Dominh K, Mangiarotti S (2001) Recent sea level change in the Mediterranean Sea revealed by Topex/Poseidon satellite altimetry. Geophys Res Lett 28:1607–1610
Church JA, White NJ, Coleman R et al (2004) Estimates of the regional distribution of sea level rise over the 1950–2000 period. J Clim 17:2609–2625
Collet I (2010) Portrait of EU coastal regions (No. 38), Eurostat
Déqué M, Devreton C, Braun A, Cariolle D (1994) The Arpege/Ifs atmosphere model—a contribution to the French community climate modeling. Clim Dyn 10:249–266
Douglas E, Kirshen P, Paolisso M, Watson C, Wiggin J, Enrici A, Ruth M (2012) Coastal flooding, climate change and environmental justice: identifying obstacles and incentives for adaptation in two metropolitan Boston Massachusetts communities. Mitig Adapt Strat Glob Change 17:537–562
EC (2002) Recommendation of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2002 concerning the implementation of Integrated Coastal Zone Management in Europe
EEA (2006) The changing faces of Europe’s coastal areas. European Environment Agency, Copenhagen
EEA (2008) Impacts of Europe’s changing climate—2008 indicator-based assessment (No. 4/2008). EEA-JRCWHO, Copenhagen
EEA (2010) The European Environment State and outlook 2010. Marine and coastal environment. EEA, Copenhagen
Eilola K, Gustafsson BG, Kuznetsov I, Meier HEM, Neumann T, Savchuk OP (2011) Evaluation of biogeochemical cycles in an ensemble of three state-of-the-art numerical models of the Baltic Sea. J Mar Syst 88:267–284
Hulme M, Dessai S (2008) Negotiating future climates for public policy: a critical assessment of the development of climate scenarios for the UK. Environ Sci Policy 11:54–70
Johns T, Royer JF, Höschel I et al (2011) Climate change under aggressive mitigation: the ENSEMBLES multi-model experiment. Clim Dyn 37:1975–2003
Jones PD, New M, Parker DE et al (1999) Surface air temperature and its variations over the last 150 years. Rev Geophys 37:173–199
King DA (2004) Climate change science: adapt, mitigate, or ignore? Science 303:176–177
L’Hévéder B, Li L, Sevault F, Somot S (2012) Interannual variability of deep convection in the Northwestern Mediterranean simulated with a coupled AORCM. Clim Dyn 1–24. doi:10.1007/s00382-012-1527-5
Lazzari P, Teruzzi A, Salon S, Campagna S, Calonaci C, Colella S, Tonani M, Crise A (2010) Pre-operational short-term forecasts for Mediterranean Sea biogeochemistry. Ocean Sci 6:25–39
Lazzari P, Solidoro C, Ibello V, Salon S, Teruzzi A, Béranger K, Colella S, Crise A (2012) Seasonal and inter-annual variability of plankton chlorophyll and primary production in the Mediterranean Sea: a modelling approach. Biogeosciences 9:217–233
Liebmann B, Dole RM, Jones C et al (2010) Influence of choice of time period on global surface temperature trend estimates. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 91:1485–1491
Ludwig W (2009) River runoff and nutrient load data sets. Estimates under WP7 socio economical scenarios (SESAME IP project No. 6.1.3). SESAME IP project, rep. n. 6.1.3
Ludwig W, Dumont E, Meybeck M, Heussner S (2009) River discharges of water and nutrients to the Mediterranean Sea: major drivers for ecosystem changes during past and future decades? Prog Oceanogr 80:199–217
Marcomini A (2011) CANTICO—Climate and local ANthropogenic drivers and impacts for the TunIsian COastal area. Final Report
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins W, Friedlingstein A, Gaye A, Gregory J, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy J, Noda A et al (2007) Global climate projections. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Nakicenovic N, Alcamo J, Davis G, De Vries B, Fenhann J, Gaffin S, Gregory K, Grübler A, Jung TY, Kram T, La Rovere EL, Michaelis H, Mori S, Morita T, Pepper W, Pitcher H, Price L, Raihi K, Roehrl A, Rogner HH, Sankovski A, Schlesinger M, Shukla P, Smith S, Swart R, Van Rooijen S, Victor N, Dadi Z (2000). Emissions Scenarios. A Special Report of Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press
Oddo P, Adani M, Pinardi N et al (2009) A nested Atlantic-Mediterranean Sea general circulation model for operational forecasting. Ocean Sci Discuss 5:461–473
Parry ML (2007) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability: contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge Univ Pr.
Pinardi N, Masetti E (2000) Variability of the large scale general circulation of the Mediterranean Sea from observations and modelling: a review. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 158:153–174
Pujol MI, Larnicol G (2005) Mediterranean sea eddy kinetic energy variability from 11 ys of altimetric data. J Mar Syst 58:121–142
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Globally complete analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice and night marine air temperature, 1871–2000. J Geophys Res 108:4407
Rayner NA, Brohan P, Parker DE et al (2006) Improved analyses of changes and uncertainties in marine temperature measured in situ since the mid-nineteenth century: the HadSST2 dataset. J Clim 19:446–469
Richards JA, Nicholls RJ (2009) Impacts of climate change in coastal systems in Europe. PESETACoastal Systems study. (EUR 24130 No. EUR 24130). EC, Luxembourg
Sanchez-Gomez E, Somot S, Josey SA et al (2011) Evaluation of Mediterranean Sea water and heat budgets simulated by an ensemble of high resolution regional climate models. Clim Dyn 1–20
Sarewitz D, Pielke RA (2007) The neglected heart of science policy: reconciling supply of and demand for science. Environ Sci Policy 10:5–16
Sevault F, Somot S, Beuvier J (2009) A regional version of the NEMO ocean engine on the Mediterranean Sea: NEMOMED8 user’s guide (No. Note de centre n°107), Groupe de Météorologie de Grande Echelle et Climat. CNRM
Somot S, Sevault F, Déqué M (2006) Transient climate change scenario simulation of the Mediterranean Sea for the twenty-first century using a high-resolution ocean circulation model. Clim Dyn 27:851–879
Tonani M, Pinardi N, Dobricic S, Pujol MI, Fratianni C (2008) A high-resolution free-surface model of the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci 4:1–14
Torresan S, Zabeo A, Rizzi J, Critto A, Pizzol L, Giove S, Marcomini A (2010) Risk assessment and decision support tools for the integrated evaluation of climate change impacts on coastal zones. In: Proceedings of the international congress on environmental modelling and software, modelling for environment’s sake. Ottawa 5–8 July. Presented at the modelling for environment’s sake, Ottawa
Tsimplis MN, Rixen M (2002) Sea level in the Mediterranean Sea: the contribution of temperature and salinity changes. Geophys Res Lett 29:2136
Uppala SM, Kallberg PW, Simmons AJ, Andrae U, Bechtold VDC, Fiorino M, Gibson JK, Haseler J, Hernandez A, Kelly GA, Li X, Onogi K, Saarinen S, Sokka N, Allan RP, Andersson E, Arpe K, Balmaseda MA, Beljaars ACM, Berg LVD, Bidlot J, Bormann N, Caires S, Chevallier F, Dethof A, Dragosavac M, Fisher M, Fuentes M, Hagemann S, Hólm E, Hoskins BJ, Isaksen L, Janssen PAEM, Jenne R, Mcnally AP, Mahfouf J-F, Morcrette J-J, Rayner NA, Saunders RW, Simon P, Sterl A, Trenberth KE, Untch A, Vasiljevic D, Viterbo P, Woollen J (2005) The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q J R Meteorol Soc 131:2961–3012
Vafeidis AT, Nicholls RJ, McFadden L, Tol RSJ, Hinkel J, Spencer T, Grashoff PS, Boot G, Klein RJT (2008) A new global coastal database for impact and vulnerability analysis to sea-level rise. J Coast Res 244:917–924
Vichi M (2009) Dataset with results of the basin scale simulations for distributions to partners involved in regional simulation (SESAME IP project No. 6.2.2), SESAME IP project. SESAME IP project, rep. n. 6.2.2
Acknowledgments
The activities described in this paper were developed in the frame of the CANTICO project, funded under the CIRCLE-MED programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10113_2013_430_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary material Figures illustrating the differences in physical and chemical variables considered in this paper and a figure representing the precipitation values for comparison between the present and the A1B climate scenarios is reported in the electronic Supplementary Material (SM). This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://link.springer.com/journal/ (PDF 6696 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamon, L., Rizzi, J., Bonaduce, A. et al. An ensemble of models for identifying climate change scenarios in the Gulf of Gabes, Tunisia. Reg Environ Change 14 (Suppl 1), 31–40 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0430-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-013-0430-x