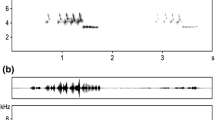
Abstract
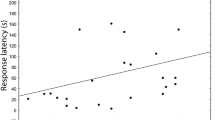
Gobius cruentatus emit sounds during agonistic interactions. In order to evaluate the effect of boat noise exposure on G. cruentatus territorial behaviour, we played a field-recorded diesel engine boat noise during aggressive encounters between an intruder and a resident fish in a laboratory-controlled tank. We tested two factors: role (resident vs. intruder) and condition (noisy vs. silent); the test animals underwent all the treatments in a round-robin design. Agonistic behavior of the residents was modified by boat noise: during the playback residents were more submissive and won less encounters than in the control (silent) condition. We suggest that sound production is an effective tool for territorial defense, since the impairment of acoustic communication due to the recreational boat noise diminished the ability of the resident to maintain its territory.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu T, Okumura T, Novarini N, Yan HY (2002) Empirical refinements applicable to the recording of fish sounds in small tanks. J Acoust Soc Am 112:3073–3082
Amorim MCP, Almada VC (2005) The outcome of male–male encounters affects subsequent sound production during courtship in the cichlid fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Anim Behav 69:595–601
Amorim MCP, Neves ASM (2008) Male painted gobies (Pomatoschistus pictus) vocalize to defend territories. Behav 145:1065–1083
Amoser S, Wysocki LE, Ladich F (2004) Noise emission during the first powerboat race in an Alpine lake and potential impact on fish communities. J Acoust Soc Am 116:3789–3797
Candolin U, Salesto T, Evers M (2007) Changed environmental conditions weaken sexual selection in sticklebacks. J Evol Biol 20:233–239
Chase I, Bartolomeo C, Dugatkin LA (1994) Aggressive interactions and inter-contest interval: how long do winners keep winning? Anim Behav 48:393–400
Codarin A, Wysocki LE, Ladich F, Picciulin M (2009) Effects of ambient and boat noise on hearing and communication in three fish species living in a marine protected area (Miramare, Italy). Mar Poll Bull 58:1880–1887
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale
Enquist M, Leimar O, Ljungberg T, Mallner Y, Segerdahl N (1990) A test of the sequential assessment game: fighting in the cichlid fish Nannacara anomala. Anim Behav 40:1–14
Gill PS, Swartz TB (2001) Statistical analyses for round robin interaction data. Can J Stat 29:321–331
Haviland-Howell G, Frankel AS, Powel CM, Bocconcelli A, Herman RL, Sayigh LS (2007) Recreational boating traffic: a chronic source of anthropogenic noise in Wilmington, North Carolina Intracoastal Waterway. J Acoust Soc Am 122:151–160
Ladich F (1997) Agonistic behaviour and significance of sounds in vocalizing fish. Mar Freshw Behav Physiol 29:87–108
Ladich F, Myrberg AA (2006) Agonistic behavior and acoustic communication. In: Ladich F, Collin S, Moller P, Kapoor BG (eds) Communication in fishes. Science Publishers, Enfield, pp 121–148
Lugli M, Yan HY, Fine ML (2003) Acoustic communication in two freshwater gobies: the relationship between ambient noise, hearing thresholds and sound spectrum. J Comp Physiol 189:309–320
Maynard Smith J (1982) Evolution and the theory of games. Cambridge University Press, New York
McBurney DH (1998) Experimental psychology. Wadsworth, Belmont
Meunier B, Yavno S, Ahmed S, Corkum LD (2009) First documentation of spawning and nest guarding in the laboratory by the invasive fish, the round goby (Neogobius melanostomus). J Great Lakes Res 35:608–612
Oliveira RF, Hirschenhauser K, Carneiro LA, Canario AVM (2002) Social modulation of androgen levels in male teleost fish. Comp Biochem Physiol B: Biochem Mol Biol 132:203–215
Ota D, Marchesan M, Casaretto L, Francese M, Ferrero EA (1999) Life style of the grass goby Zosterisessor ophiocephalus (Pisces, Gobiidae). Boll Soc Adriat Sci 78:183–206
Ottoni EB (2000) EthoLog 2.2: A tool for the transcription and timing of behavior observation sessions. Behav Res Meth Instr Comp 32:446–449
Picciulin M, Sebastianutto L, Costantini M, Rocca M, Ferrero EA (2006) Aggressive territorial ethogram of the red-mouthed goby, Gobius cruentatus (Gmelin 1789). Electron J Ichthyol 2:38–49
Picciulin M, Sebastianutto L, Codarin A, Farina A, Ferrero EA (2010) In-situ behavioral responses to boat noise exposure of Gobius cruentatus (Gmelin, 1789; fam. Gobiidae) and Chromis chromis (Linnaeus, 1758; fam. Pomacentridae) living in a Marine Protected Area. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 386:125–132
Popper AN, Fewtrell J, Smith ME, McCauley RD (2004) Anthropogenic sound: effects on the behavior and physiology of fishes. J Mar Sci Technol 37:35–40
Raffinger E, Ladich F (2009) Acoustic threat displays and agonistic behaviour in the red-finned loach Yasuhikotakia modesta. J Ethol 27:239–247
Richardson WJ, Würsig B (1997) Influences of man-made noise and other human actions on cetacean behavior. Mar Freshwat Behav Physiol 29:183–209
Rocca M (2001) Caratterizzazione del comportamento e delle emissioni acustiche in Gobius cruentatus (Gmelin, 1789) in contesto agonistico. Dissertation, University of Trieste
Sebastianutto L, Picciulin M, Costantini M, Rocca M, Ferrero EA (2008) Four types of sounds for one winner: vocalizations during territorial behaviour in the red-mouthed goby Gobius cruentatus (Pisces: Gobiidae). Acta ethol 11:115–121
Slabbekoorn H, Bouton N, van Opzeeland I, Coers A, ten Cate C, Popper AN (2010) A noisy spring: the impact of globally rising underwater sound levels on fish. Trends Ecol Evol 25(7):419–27
Tortonese E (1975) Bavose e ghiozzi. In: Fauna d’Italia. Osteichthyes (Pesci Ossei). Calderini, Bologna
Valinksy W, Ridgley L (1981) Function of sound production by the skunk loach Botia horae (Pisces: Cobitidae). Z Tierpsychol 55:161–172
Vasconcelos RO, Amorim MCP, Ladich F (2007) Effects of ship noise on the detectability of communication signals in the Lusitanian toadfish. J Exp Biol 210:2104–2112
Vasconcelos RO, Simones JM, Almada VC, Fonseca PJ, Amorim MCP (2010) Vocal behavior during territorial intrusions in the Lusitanian Toadfish: boatwhistles also function as territorial ‘keep-out’ signals. Ethology 116:155–165
Wilkins HKA, Myers AA (1991) The distribution of Gobies (Teleostei, Gobiidae). In: Myers AA, Little C, Costello MJ, Partridge JC (eds) The ecology of Lough Hyne. Royal Irish Academy, Dublin, pp 107–115
Wilkins HKA, Myers AA (1993) Shelter utilisation by Gobius cruentatus and Thorogobius ephippiatus (Teleostei: Gobiidae). J Fish Biol 43:763–773
Wong BBM, Candolin U, Lindstrom K (2007) Environmental deterioration compromises socially enforced signals of male quality in three-spined sticklebacks. Am Nat 170:184–189
Wysocki LE, Codarin A, Ladich F, Picciulin M (2009) Sound pressure and particle acceleration audiograms in three marine fish species from the Adriatic Sea. J Acoust Soc Am 126:2100–2107
Acknowledgments
This study was part of a project to monitor human-made noise in Marine Protected Areas supported by the Italian Ministry for Environment, Territory and Sea. We would like to thank Maurizio Spoto and the Miramare Natural Marine Reserve staff for technical assistance, Elena Pangaro for her support in data collection, Antonio Codarin for help in acoustic analyses, MPC Amorim for critical reading and valuable comments, and Valerie Lesk for English proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebastianutto, L., Picciulin, M., Costantini, M. et al. How boat noise affects an ecologically crucial behaviour: the case of territoriality in Gobius cruentatus (Gobiidae). Environ Biol Fish 92, 207–215 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9834-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-011-9834-y