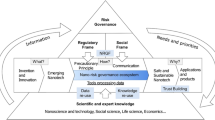
Abstract
Various emerging technologies challenge existing governance processes to identify, assess, and manage risk. Though the existing risk-based paradigm has been essential for assessment of many chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear technologies, a complementary approach may be warranted for the early-stage assessment and management challenges of high uncertainty technologies ranging from nanotechnology to synthetic biology to artificial intelligence, among many others. This paper argues for a risk governance approach that integrates quantitative experimental information alongside qualitative expert insight to characterize and balance the risks, benefits, costs, and societal implications of emerging technologies. Various articles in scholarly literature have highlighted differing points of how to address technological uncertainty, and this article builds upon such knowledge to explain how an emerging technology risk governance process should be driven by a multi-stakeholder effort, incorporate various disparate sources of information, review various endpoints and outcomes, and comparatively assess emerging technology performance against existing conventional products in a given application area. At least in the early stages of development when quantitative data for risk assessment remain incomplete or limited, such an approach can be valuable for policymakers and decision makers to evaluate the impact that such technologies may have upon human and environmental health.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bates M, Grieger KD, Trump BD, Keisler JM, Plourde KJ, Linkov I (2015) Emerging technologies for environmental remediation: integrating data and judgment. Environ Sci Technol 50:349–358
Blaunstein R, Trump B, Linkov I (2014) Nanotechnology risk management: an insurance industry perspective. In: Hull M, Bowman D (eds) Nanotechnology environmental health and safety: risks, regulation, and management, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 247–263
Calvert J, Martin P (2009) The role of social scientists in synthetic biology. EMBO Rep 10(3):201–204
Canis L, Linkov I, Seager TP (2010) Application of stochastic multiattribute analysis to assessment of single walled carbon nanotube synthesis processes. Environ Sci Technol 44(22):8704–8711
Csiszar SA, Meyer DE, Dionisio KL, Egeghy P, Isaacs KK, Price PS et al (2016) Conceptual framework to extend life cycle assessment using near-field human exposure modeling and high-throughput tools for chemicals. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11922–11934
Cummings CL, Kuzma J (2017) Societal risk evaluation scheme (SRES): scenario-based multi-criteria evaluation of synthetic biology applications. PLoS ONE 12:e0168564
Cummings CL, Lin SH, Trump BD (2017) Public perceptions of climate geoengineering: a systematic review of the literature. Clim Res 73(3):247–264
Epstein MM, Vermeire T (2016) Scientific opinion on risk assessment of synthetic biology. Trends Biotechnol 34(8):601–603
Falkner R, Jaspers N (2012) Regulating nanotechnologies: risk, uncertainty and the global governance gap. Global Environ Politics 12(1):30–55
Ferson S, Sentz K (2016) Epistemic uncertainty in agent-based modeling. In: 7th international workshop on reliable engineering computing
Grieger K, Hansen SF, Baun A (2009) The known unknowns of nanomaterials: describing and characterizing uncertainty within environmental, health and safety risks. Nanotoxicology 3:222–233
Gronvall GK (2018) Safety, security, and serving the public interest in synthetic biology. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1–4
Hristozov DR, Gottardo S, Critto A, Marcomini A (2012) Risk assessment of engineered nanomaterials: a review of available data and approaches from a regulatory perspective. Nanotoxicology 6(8):880–898
Hristozov D, Gottardo S, Semenzin E, Oomen A, Bos P, Peijnenburg W et al (2016) Frameworks and tools for risk assessment of manufactured nanomaterials. Environ Int 95:36–53
König H, Frank D, Heil R, Coenen C (2016) Synthetic biology’s multiple dimensions of benefits and risks: implications for governance and policies. In: Boldt J (ed) Synthetic biology. Springer Fachmedien, Wiesbaden, pp 217–232
Kuiken T, Dana G, Oye K, Rejeski D (2014) Shaping ecological risk research for synthetic biology. J Environ Stud Sci 4(3):191–199
Kuzma J (2015) Translational governance research for synthetic biology. J Responsible Innov 2(1):109–112
Kuzma J, Paradise J, Ramachandran G, Kim J, Kokotovich A, Wolf SM (2008) An integrated approach to oversight assessment for emerging technologies. Risk Anal 28(5):1197–1220
Linkov I, Bates ME, Canis LJ, Seager TP, Keisler JM (2011) A decision-directed approach for prioritizing research into the impact of nanomaterials on the environment and human health. Nat Nanotechnol 6(12):784
Linkov I, Bates ME, Trump BD, Seager TP, Chappell MA, Keisler JM (2013) For nanotechnology decisions, use decision analysis. Nano Today 8(1):5–10
Linkov I, Trump B, Jin D, Mazurczak M, Schreurs M (2014) A decision-analytic approach to predict state regulation of hydraulic fracturing. Environ Sci Eur 26(1):20
Linkov I, Trump BD, Wender BA, Seager TP, Kennedy AJ, Keisler JM (2017) Integrate life-cycle assessment and risk analysis results, not methods. Nat Nanotechnol 12(8):740–743
Linkov I, Trump BD, Poinsatte-Jones K, Florin MV (2018) Governance strategies for a sustainable digital world. Sustainability 10(2):440
Malloy T, Trump BD, Linkov I (2016) Risk-based and prevention-based governance for emerging materials. Environ Sci Technol 50:6822–6824
Malsch I, Mullins M, Semenzin E, Zabeo A, Hristozov D, Marcomini A (2018) Decision support for international agreements regulating nanomaterials. NanoEthics 12(1):39–54
Mandel G, Marchant GE (2014) The living regulatory challenges of synthetic biology. Iowa L Rev 100:155
Mohan M, Trump BD, Bates ME, Monica JC Jr, Linkov I (2012) Integrating legal liabilities in nanomanufacturing risk management. Environ Sci Technol 46(15):7955–7962
Mukunda G, Oye KA, Mohr SC (2009) What rough beast? Synthetic biology, uncertainty, and the future of biosecurity. Politics Life Sci 28(2):2–26
National Research Council (1983) Risk assessment in the federal government: managing the process. National Academies Press, Washington, DC
National Research Council (2011) Sustainability and the U.S. EPA. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.17226/13152
Oye KA (2012) Proactive and adaptive governance of emerging risks: the case of DNA synthesis and synthetic biology. International Risk Governance Council, Geneva
Palma-Oliveira JM, Trump BD, Wood MD, Linkov I (2017) Community-driven hypothesis testing: a solution for the tragedy of the anticommons. Risk Anal 38:620–634
Renn O (2005) White paper on risk governance: towards an integrative approach. International Risk Governance Council, Geneva
Renn O, Klinke A, van Asselt M (2011) Coping with complexity, uncertainty, and ambiguity in risk governance: a synthesis. Ambio 40:231–246
Rycroft T, Trump B, Poinsatte-Jones K, Linkov I (2018) Nanotoxicology and nanomedicine: making development decisions in an evolving governance environment. J Nanopart Res 20(2):52
Schmidt M, Kelle A, Ganguli-Mitra A, de Vriend H (eds) (2009) Synthetic biology: the technoscience and its societal consequences. Springer, New York
Scott-Fordsmand JJ, Pozzi-Mucelli S, Tran L, Aschberger K, Sabella S, Vogel U et al (2014) A unified framework for nanosafety is needed. Nano Today 9(5):546–549
Seager TP, Linkov I (2008) Coupling multicriteria decision analysis and life cycle assessment for nanomaterials. J Ind Ecol 12(3):282–285
Seager TP, Trump BD, Poinsatte-Jones K, Linkov I (2017) Why life cycle assessment does not work for synthetic biology. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b01604
Shatkin JA (2008) Informing environmental decision making by combining life cycle assessment and risk analysis. J Ind Ecol 12(3):278–281
Shatkin JA, Ong KJ, Beaudrie C, Clippinger AJ, Hendren CO, Haber LT et al (2016) Advancing risk analysis for nanoscale materials: report from an international workshop on the role of alternative testing strategies for advancement. Risk Anal 36(8):1520–1537
Siegrist M, Keller C, Kastenholz H, Frey S, Wiek A (2007) Laypeople’s and experts’ perception of nanotechnology hazards. Risk Anal 27(1):59–69
Small M, Stern PC, Bomberg E, Christopherson SM, Goldstein BD, Israel AL, Jackson RB, Krupnick A, Mauter MS, Nash J, North DW, Olmstead SM, Prakash A, Rabe B, Richardson N, Tierney S, Webler T, Wong-Parodi G, Zielinska B (2014) Risks and risk governance in unconventional shale gas development. Environ Sci Technol 48:8289–8297
Subramanian V, Semenzin E, Hristozov D, Marcomini A, Linkov I (2014) Sustainable nanotechnology: defining, measuring and teaching. Nano Today 9(1):6–9
Tait J (2009) Governing synthetic biology: processes and outcomes. In: Schmidt M (ed) Synthetic biology. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 141–154
Tait J (2012) Adaptive governance of synthetic biology. EMBO Rep 13(7):579–579
Tervonen T, Linkov I, Figueira JR, Steevens J, Chappell M, Merad M (2009) Risk-based classification system of nanomaterials. J Nanopart Res 11(4):757–766
Trump BD (2017) Synthetic biology regulation and governance: lessons from TAPIC for the United States, European Union, and Singapore. Health Policy 121(11):1139–1146
Trump BD, Linkov F, Edwards RP, Linkov I (2015) Not a Humbug: the evolution of patient-centred medical decision-making. Evid Based Med 20(6):193–197
Trump BD, Cummings C, Kuzma J, Linkov I (2017) A decision analytic model to guide early-stage government regulatory action: applications for synthetic biology. Regul Gov. https://doi.org/10.1111/rego.12142
Trump BD, Hristozov D, Malloy T, Linkov I (in press) Risk associated with engineered nanomaterials: different tools for different ways to govern. Nano Today
Vallero D (2015) Environmental biotechnology: a biosystems approach. Academic Press, Amsterdam
Wilson MP, Schwarzman MR (2009) Toward a new US chemicals policy: rebuilding the foundation to advance new science, green chemistry, and environmental health. Environ Health Perspect 117(8):1202
Wood MD, Plourde K, Larkin S, Egeghy PE, Williams AJ, Zemba V, Linkov I, Vallero DA (in press) Advances on a decision analytic approach to exposure-based chemical prioritization. Risk Anal
Yatsalo B, Gritsyuk S, Sullivan T, Trump B, Linkov I (2016) Multi-criteria risk management with the use of DecernsMCDA: methods and case studies. Environ Syst Decis 36(3):266–276
Acknowledgements
The authors were participants in the “Risk Policy Forum on Key Enabling Technologies” hosted by the Society for Risk Analysis, and Ca Foscari University, Venice, Italy, on March 2017. This workshop and paper were part of a SRA New Initiative Project. The authors thank the conference attendees and panelists that drove discussions, as well as Emily Wells for her editorial assistance, and George Shephard for his figure design assistance. The views expressed within this paper are solely the opinions of the authors, and are not necessarily representative of their organizational affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linkov, I., Trump, B.D., Anklam, E. et al. Comparative, collaborative, and integrative risk governance for emerging technologies. Environ Syst Decis 38, 170–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-018-9686-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-018-9686-5