Abstract
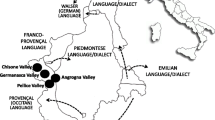
An ethnobotanical field study on the traditional uses of wild medicinal and food plants was conducted in three linguistically distinct mountainous communities located at the East End of the Occitan macro-area, in the Western Italian Alps. Interviews with a total of 81 mid-aged and elderly informants were undertaken using standard ethnobotanical methods. The uses of 92 vascular plants belonging to 40 different plant families were recorded. Comparison of the collected data with the ethnobotanical findings of previously conducted studies in other Occitan/Provençal valleys (specifically the Stura and Varaita valleys) has shown that nearly the half of the uses recorded in this study were not reported in other valleys, strongly suggesting a heterogeneous character to Occitan ethnobotany. The specific uses of certain wild plants as famine foods and medicines in this region are highlighted.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Madeiros PM, Soldati GT, Alencar NL, Vandebroek I, Pieroni A, Hanazaki N, de Albuquerque UP (2012) The use of medicinal plants by migrant people: adaptation, maintenance, and replacement. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med ID 807452
González-Tejero M, Casares-Porcel M, Sánchez-Rojas CP, Ramiro-Gutiérrez JM, Molero-Mesa J, Pieroni A, Giusti ME, Censorii C, de Pasquale C, Della D, Paraskeva-Hadijchambi D, Hadjichambis A, Houmani Z, El-Demerdash M, El-Zayat M, Hmamouchi M, El-Johri S (2008) Medicinal plants in the Mediterranean area: synthesis of the results of the project Rubia. J Ethnopharmacol 116:341–357
Grassi C (1969) Parlà du kyé. Un’isola linguistica provenzale nelle Valli monregalesi. Studi Linguistici Salentini 2:128–138
Hammer K, Laghetti G, Pignone D (eds) (2011) Linguistic islands and plant genetic resources. The case of the arbëreshë. Aracne, Rome
International Society of Ethnobiology (2008) Code of Ethics. Available at: http://ethnobiology.net/code-of-ethics/code-in-english/ (January 2012)
Kujawska M, Zamudio F, Hilgert N (2012) Honey-based mixtures used in home medicine by non-indigenous population of Misiones, Argentina. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med ID 579350
Laghetti G, Pignone D, De Lisi A, Cifarelli S, Faslia N, Hammer K (2011) Collecting crop genetic resources in Italian towns of Albanian origin across the Molise, Calabria and Sicily regions. Genet Res Crop Evol 58:139–152
Mattirolo O (1918) Phytolalimurgia Pedementana ossia Censimento delle Specie vegetali alimentari della Flora spontanea del Piemonte. Ann Reale Acad Agric Torino 61:1–180. Reprint Gallino B, Pallavicini, G (eds) (2001) Blue Edizioni, Peveragno
Musset D, Dore D (2006) La mauve et l’erba Bianca. Une introduction aux enquêtes ethnobotaniques suivi de l’inventaire de plantes utiles dans la vallée Stura. Musée departmental ethnologique de Haute-Provence, Salagon, France
Nebel S, Pieroni A, Heinrich M (2006) Ta chòrta: wild edible greens used in the Graecanic area in Calabria, Southern Italy. Appetite 47:333–342
Pieroni A, Giusti ME (2009) Alpine ethnobotany in Italy: traditional knowledge of gastronomic and medicinal plants among the Occitans of the upper Varaita valley, Piedmont. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 5:32
Pieroni A, Gray C (2008) Herbal and food folk medicines of the Russlanddeutschen living in Künzelsau/Taläcker, South-Western Germany. Phytother Res 22:889–901
Pieroni A, Vandebroek I (2007) Traveling plants. The ethnobiology and ethnopharmacy of human migrations. Berghahn, Oxford, New York
Pieroni A, Quave C, Nebel S, Heinrich M (2002a) Ethnopharmacy of ethnic Albanians (Arbëreshë) in northern Basilicata (southern Italy). Fitoterapia 73:217–241
Pieroni A, Nebel S, Quave C, Münz H, Heinrich M (2002b) Ethnopharmacology of liakra, traditional weedy vegetables of the Arbëreshë of the Vulture area in southern Italy. J Ethnopharmacol 81:165–185
Pieroni A, Giusti ME, Münz H, Lenzarini C, Turkovic G, Turkovic A (2003) Ethnobotanical knowledge of the Istro-Romanians of Žejane in Croatia. Fitoterapia 74:710–719
Pieroni A, Quave C, Giusti ME (2011) Cross-cultural ethnobiology in the Western Balkans: medical ethnobotany and ethnozoology among Albanians and Serbs in the Pešter plateau, Sandžak, south-western Serbia. Hum Ecol 39:333–349
Pignatti S (1997) Flora d’Italia. Edagricole, Bologna
Russell Bernard H (2005) Research methods in anthropology. Qualitative and quantitative approaches. Altamira Press, Walnut Creek
Stevens, PF (2001, onwards) Angiosperm phylogeny website. Version 9, June 2008. http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/
Szabó TA, Péntek J (1976) Ezerjófű. Etnobotanikai útmutató. Kriterion Könyvkiadó, Bucharest
Toso F (2006) Lingue d’Europa. La pluralità linguistica dei Peasi europei fra passato e presente. Baldini Castoldi Dalai, Milan
Toso F (2008a) ll brigasco e l’olivettese tra classificazione scientifica e manipolazioni politico-amministrative. Intemelion 14:103–134
Toso F (2008b) Le minoranze linguistiche in Italia. Il Mulino, Bologna
Zamudio F, Kujawska M, Hilgert NI (2010) Honey as medicinal and food resource. Comparison between Polish and multiethnic settlements of the Atlantic Forest, Misiones, Argentina. Open Complement Med J 2:58–73
Acknowledgments
Special thanks are due to all participants, who graciously agreed to share their TK, and to all of the students who gathered the data in the field, including plant specimens, as well as video recordings: Svetlana Noskova, Roberta Nanu, Elena Massaia, Federica Bolla, Alberto Capelli, Tommaso Malfa, Giulio Di Sabato, Katharina Stoeckel, Katharina Zahn, Eran Kalmanson, Richard Haubenberger, Florian Ehn, Andrea Gaggero, Wilfried Rembangouet, Valentina Bosia, Anastasia Ruzaykina, Adriana Zanchi, Silvia Paoli, Gaia Lochetti, Giorgia Catalano, Francesca Selvaggio, Federico Battaglia, Elena Fachino, Andrea Masino, Federico Mina, and Martina Spreafico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattalia, G., Quave, C.L. & Pieroni, A. Traditional uses of wild food and medicinal plants among Brigasc, Kyé, and Provençal communities on the Western Italian Alps. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60, 587–603 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-012-9859-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-012-9859-x