Abstract
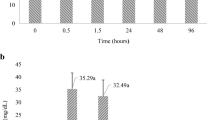
The onset of and recovery from physiological stress in Liocarcinus depurator (Decapoda: Portunidae), that were trawled and subjected to emersion during fishing activities, was analysed in a field study in the Northern Adriatic Sea. Our working hypothesis intended to assess the development of physiological impairment due to air exposure during sorting operations, and the possible recovery trajectories after the return to sea of this by-caught species. The protocol we used included experimental trawling and quantification of physiological stress indicators (haemolymph concentrations of l-lactate, d-glucose, ammonia and pH) under different seasonal conditions. Immediately after being caught, when the fishing net was emptied on board, L. depurator showed higher physiological imbalance in the summer vs. winter experiments, highlighting the immediate effect of temperature shock due to the difference in temperature between the sea bottom and the deck (15–18 and 2°C in summer and winter, respectively). Experimental animals in the permanently emersed condition exhibited a progressive disruption of homeostasis in both seasons, as confirmed by a significant increase in lactate and a decrease in the pH of the haemolymph as a function of the emersion time. Ammonia levels were almost stable in the summer, when the physiological limits of this metabolite were reached immediately after animals were caught. In the winter, a significant increase in ammonia was observed over the time. This pattern can be attributed to the impairment of gill function, resulting in suffocation (manifested by marked haemolymph acidosis) and reduced ammonia excretion. Glucose concentration was revealed to be stable during air exposure in both seasons, though a higher concentration was recorded in the summer compared to the winter. The recovered individuals tended to return to pre-caught values for all of the haemolymph parameters we measured, though with different trajectories in the two seasons. From these results, we conclude that temperature shock, coupled with air exposure, influenced the ultimate stress level of this species to a greater extent than other effects of fishing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmann, M. & P. G. Moore, 2001. Survival of decapod crustaceans discarded in the Nephrops fishery of the Clyde Sea area, Scotland. ICES Journal of Marine Science 58: 163–171.
Bergmann, M., D. J. Beare & P. G. Moore, 2001a. Damage sustained by epibenthic invertebrates discarded in the Nephrops fishery of the Clyde Sea, Scotland. Journal of Sea Research 45: 105–118.
Bergmann, M., A. C. Taylor & P. G. Moore, 2001b. Physiological stress in decapod crustaceans (Munida rugosa and Liocarcinus depurator) discarded in the Clyde Nephrops fishery. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 259: 215–229.
Bergmann, M., S. K. Wieczorek, P. G. Moore & A. R. J. Atkinson, 2002a. Discard composition of the Nephrops fishery in the Clyde Sea area, Scotland. Fisheries Research 57: 169–183.
Bergmann, M., S. K. Wieczorek, P. G. Moore & R. J. A. Atkinson, 2002b. Utilization of invertebrates discarded from the Nephrops fishery by variously selective benthic scavengers in the west of Scotland. Marine Ecology Progress Series 233: 185–198.
Broadhurst, M. K., P. Suuronen & A. Hulme, 2006. Estimating collateral mortality from towed fishing gear. Fish and Fisheries 7: 180–218.
Cameron, J. N., 1979. Excretion of CO2 in water-breathing animals: a short review. Marine Biology Letters 1: 3–13.
Chung, J. S. & N. Zmora, 2008. Functional studies of crustacean hyperglycemic hormones (CHHs) of the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus—the expression and release of CHH in eyestalk and pericardial organ in response to environmental stress. FEBS J 275: 693–704.
Danford, A. R., L. Hagerman & R. F. Uglow, 2002. Effects of emersion and elevated haemolymph ammonia on haemocyanin-oxygen affinity of Cancer pagurus. Marine Biology 141: 1019–1027.
deJuan, S., S. F. Thrush & M. Demestre, 2007. Functional changes as indicators of trawling disturbance on a benthic community located in a fishing ground (NW Mediterranean Sea). Marine Ecology Progress Series 334: 117–129.
Demestre, M., P. Sánchez & M. J. Kaiser, 2000. The behavioural response of benthic scavengers to otter-trawling disturbance in the Mediterranean. In Kaiser, M. J. & S. J. de Groot (eds), Effects of Fishing on Non-Target Species and Habitats. Blackwell Science, Oxford: 121–129.
Dulvy, N. K. & J. D. Reynolds, 2002. Predicting Extinction vulnerability in skates. Conservation Biology 16: 440–450.
Durand, F., F. Chausson & M. Regnault, 1999. Increases in tissue free amino acid levels in response to prolonged emersion in marine crabs: an ammonia-detoxifying process efficient in the intertidal Carcinus maenas but not in the subtidal Necora puber. Journal of Experimental Biology 202: 2191–2202.
Durand, F., N. Devillers, F. H. Lallier & M. Regnault, 2000. Nitrogen excretion and changes in blood components during emersion of the subtidal spider crab Maja squinado (L.). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology 127A: 259–271.
Giomi, F., S. Raicevich, A. Ferrarese, F. Pranovi, P. Di Muro & M. Beltramini, 2007. Structural and functional heterogeneity of hemocyanin: intra- and inter-specific comparison on four species of portunid crabs (Crustacea: Portunidae). Marine Biology 151: 1237–1247.
Giomi, F., S. Raicevich, O. Giovanardi, F. Pranovi, P. Di Muro & M. Beltramini, 2008. Catch me in winter! Seasonal variation in air temperature severely enhances physiological stress and mortality of species subjected to sorting operations and discarded during annual fishing activities. Hydrobiologia 606: 195–202.
Hagerman, L., T. Søndergaard, K. Weile, D. Hosie & R. F. Uglow, 1990. Aspects of blood physiology and ammonia excretion in Nephrops norvegicus under hypoxia. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology 97: 51–55.
Hall, S. J., D. Raffaelli, M. R. Robertson & D. J. Basford, 1990. The role of the predatory crab Liocarcinus depurator in a food web. Journal of Animal Ecology 59: 421–438.
Harris, R. R. & M. B. Andrews, 2005a. Physiological changes in the Norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus (L.) escaping and discarded from commercial trawls on the West Coast of Scotland 1 Body fluid volumes and haemolymph composition after capture and during recovery. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 320: 179–193.
Harris, R. R. & M. B. Andrews, 2005b. Physiological changes in the Norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus (L.) escaping and discarded from commercial trawls on the West Coast of Scotland II Disturbances in haemolymph respiratory gases, tissue metabolites and swimming performance after capture and during recovery. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 320: 195–210.
Harris, R. R. & M. Ulmestrand, 2004. Discarding Norway lobster (Nephrops norvegicus L.) through low salinity layers—mortality and damage seen in simulation experiments. ICES Journal of Marine Science 67: 127–139.
Haupt, P., S. L. Brouwer, G. M. Banch & G. Gäde, 2006. Effects of exposure to air on the escape behaviour and haemolymph chemistry of the South African Cape Lobster Jasus lalandii. Fisheries Research 81: 210–218.
Henry, R. P. & M. G. Wheatly, 1992. Interaction of respiration, ion regulation, and acid-base balance in everyday life of aquatic crustaceans. American Zoologist 32: 407–416.
Kelleher, K., 2005. Discards in the world’s marine Fisheries: an update. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No 470. Rome.
Lund, H. S., T. Wang, T. Chang, L. F. Pedersen, E. W. Taylor, P. B. Pedersen & D. J. McKenzie, 2009. Recovery by the Norway lobster Nephrops norvegicus (L.) from physiological stresses of trawling: influence of season and live storage position. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 373: 124–132.
MacDonald, D., M. Little, N. C. Eno & K. Hiscock, 1996. Disturbance of benthic species by fishing activities: sensitivity index. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 6: 257–268.
Mangum, C. P., 1985. Molting in the blue crab Callinectes sapidus: a collaborative study of intermediary metabolism, respiration and cardiovascular function, and ion transport. Preface. Journal of Crustacean Biology 5: 185–187.
McMahon, B. R. & J. L. Wilkens, 1983. Ventilation, perfusion and oxygen uptake. In Bliss, D. E. (ed.), The Biology of Crustacea. Vol 5: Internal Anatomy and Physiological Regulation. Academic Press, New York: 290–372.
McMahon, B. R., 2001. Respiratory and circulatory compensation to hypoxia in crustaceans. Respiration Physiology 128: 349–364.
Pranovi, F., S. Raicevich, G. Franceschini, P. Torricelli & O. Giovanardi, 2001. Discard composition and damage to non-target species in the “rapido” trawl fishery. Marine Biology 139: 863–875.
Ramsay, K., M. J. Kaiser, A. D. Rijndorp, J. A. Craeymeersch & J. Ellis, 2000. Impact of trawling on population of the invertebrate scavenger Asteria rubens. In Kaiser, M. J. & S. J. de Groot (eds), Effects of Fishing on Non-Target Species and Habitats. Blackwell Science, Oxford: 151–162.
Ridgway, I. D., A. C. Taylor, R. J. A. Atkinson, G. D. Stentinford, E. S. Chang, S. A. Chang & D. M. Neil, 2006. Morbidity and mortality in Norway lobsters, Nephrops norvegicus: physiological, immunological and pathological effects of aerial exposure. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 328: 251–264.
Rufino, M. M., P. Abelló, A. B. Yule & P. Torres, 2005. Geographic. Bathymetric and inter-annual variability in the distribution of Liocarcinus depurator (Brachyura: Portunidae) along the Mediterranena coast line of the Iberian Peninsula. Scientia Marina 69: 503–518.
Santos, E. A. & R. Keller, 1993. Effect of exposure to atmospheric air on blood glucose and lactate concentration in two crustacean species: a role of the crustacean hyperglycaemic hormone (CHH). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology 106A: 343–347.
Šimunović, A., 1997. Quantitative and qualitative investigations of benthic communities in the areas of mobile bottoms of the Adriatic Sea. Acta Adriatica 38(1): 77–194.
Tukey, V.W., 1953. The Problem of Multiple Comparisons. Mimeographed monograph, Princeton University.
Webster, S. G., 1996. Measurement of crustacean hyperglycaemic hormone levels in the edible crab Cancer pagurus during emersion stress. Journal of Experimental Biology 199: 1579–1585.
Acknowledgements
F. Da Ponte, G. Franceschini, A. Granzotto, M. Zucchetta and the captain and the crew of the F/V Ca Moro kindly helped during sampling operations. S. Mattiello technically supported the determination of metabolite concentrations. Dr. R. Precali, Institute Ruder Boskovic (Rovinj, Croatia), provided oceanographic data. Dr. G. Fabi, Istituto di Scienze del Mare (Ancona, Italy), provided data on L. depurator’s spatial distribution in the central and northern Adriatic Sea. Research activities were supported by the Italian Ministry of Agricultural Policies (DG Fisheries and Aquaculture, Pr. 5A34) and University of Padova grants (60A06-1337/05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handing editor: Stuart Jenkins
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raicevich, S., Giomi, F., Pranovi, F. et al. Onset of and recovery from physiological stress in Liocarcinus depurator after trawling and air exposure under different seasonal conditions. Hydrobiologia 664, 107–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0590-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0590-3