Abstract
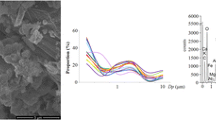
Size segregated particulate samples of atmospheric aerosols in urban site of continental part of Balkans were collected during 6 months in 2008. Six stages impactor in the size ranges: Dp ≤ 0.49 μm, 0.49 < Dp ≤ 0.95 μm, 0.95 < Dp ≤ 1.5 μm, 1.5 < Dp ≤ 3.0 μm, 3.0 < Dp ≤ 7.2 μm, and 7.2 < Dp ≤ 10.0 μm was applied for sampling. ICP-MS was used to quantify elements: Al, As, Bi, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Ga, K, Li, Na, Ni, Mg, Mn, Pb, Sb, V, and Zn. Two main groups of elements were investigated: (1) K, V, Ni, Zn, Pb, As, and Cd with high domination in nuclei mode indicating the combustion processes as a dominant sources and (2) Al, Fe, Ca, Mg, Na, Cr, Ga, Co, and Li in coarse mode indicating mechanical processes as their main origin. The strictly crustal origin is for Mg, Fe, Ca, and Co while for As, Cd, K, V, Ni, Cu, Pb, and Zn dominates the anthropogenic influence. The PCA analysis has shown that main contribution is of resuspension (PC1, σ2 ≈ 30 %) followed by traffic (PC2, σ2 ≈ 20 %) that are together contributing around 50 % of elements in the investigated urban aerosol. The EF model shows that major origin of Cd, K, V, Ni, Cu, Pb, Zn, and As in the fine mode is from the anthropogenic sources while increase of their contents in the coarse particles indicates their deposition from the atmosphere and soil contamination. This approach is useful for the assessment of the local resuspension influence on element’s contents in the aerosol and also for the evaluation of the historical pollution of soil caused by deposition of metals from the atmosphere.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Allen AG, Nemitz E, Shi JP, Harrison RM, Greenwood JC (2001) Size distributions of trace metals in atmospheric aerosols in the United Kingdom. Atmos Environ 35:4581–4591
Aničić M, Tasić M, Frontasyeva MV, Tomašević M, Rajšić S, Mijić Z, Popović A (2009) Active moss biomonitoring of trace elements with Sphagnum girgensohnii Moss bags in relation to atmospheric bulk deposition in Belgrade, Serbia. Environ Pollut 157:673–679
Belis CA, Karagulian F, Larsen BR, Hopke PK (2013) Critical review and meta-analysis of ambient particulate matter source apportionment using receptor models in Europe. Atmos Environ 69:94–108
Brüggemann E, Gerwig H, Gnauk T, Müller K, Herrmann H (2009) Influence of seasons, air mass origin and day of the week on size-segregated chemical composition of aerosol particles at a kerbside. Atmos Environ 43:2456–2463
Buccolieri A, Buccolieri G, Cardellicchio N, Dell’Atti A, Florio ET (2005) Metals content in atmospheric particulate matter collected from an urban area of Abulia (Southern Italy). Ann Chim 95:15–25
Contini D, Belosi F, Gambaro A, Cesari D, Stortini AM, Bove MC (2012) Comparison of PM10 concentrations and metal content in three different sites of the Venice Lagoon: an analysis of possible aerosol sources. J Environ Sci 24:1954–1965
Contini D, Cesari D, Genga A, Siciliano M, Lelpo P, Guascito MR, Conte M (2014) Source apportionment of size-segregated atmospheric particles based on the major water-soluble components in Lecce (Italy). Sci Total Environ 472(2014):248–261
Đorđević D, Vukmirović Z, Tosić I, Unkasević M (2004a) Contribution of dust transport and resuspension to particulate matter levels in the Mediterranean atmosphere. Atmos Environ 38:3637–3645
Đorđević D, Radmanović D, Mihajlidi-Zelić A, Ilić M, Pfendt P, Vukmirović Z, Polić P (2004b) Associations of trace elements in aerosol at the south Adriatic coast. Environ Chem Lett 2:147–150
Đorđević D, Mihajlidi-Zelić A, Relić D, Lj I, Huremović J, Stortini AM, Gambaro A (2012) Size-segregated mass concentration and water soluble inorganic ions in an urban aerosol of the Central Balkans (Belgrade). Atmos Environ 46:309–317
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Handler M, Puls C, Zbiral J, Marr I, Puxbaum H, Limbeck A (2008) Size composition of particulate emission from motor vehicles in the Kaisermühlen-Tunnel, Vienna. Atmos Environ 42:2173–2186
Hlavay J, Polyák K, Bódog I, Molnár Á, Mészáros E (1996) Distribution of trace elements in filter-collected aerosol samples. Fresenius J Anal Chem 354:227–232
Koulouri E, Saarikoski S, Theodosi C, Markaki Z, Gerasopoulos E, Kouvarakis G, Mäkelä T, Hillamo R, Mihalopoulus N (2008) Chemical composition and sources of fine and coarse aerosol particles in the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos Environ 42:6542–6550
Lawrence S, Sokhi R, Ravindra K, Mao H, Prain HD, Bull ID (2013) Source apportionment of traffic emissions of particulate matter using tunnel measurements. Atmos Environ 77:548–557
Ning Z, Polidori A, Schauer JJ, Sioutas C (2008) Emission factors of PM species based on freeway measurements and comparison with tunnel and dynamometer studies. Atmos Environ 42:3099–3114
Ntziachristos L, Ning Z, Geller MD, Sheesley RJ, Schauer JJ, Sioutas C (2007) Fine, ultrafine and nanoparticle trace element compositions near a major freeway with a high heavy-duty diesel fraction. Atmos Environ 41:5684–5696
Moffet RC, Desyaterik Y, Hopkins RJ, Tivanski AV, Gilles MK, Wang Y, Shutthanandan V, Molina LT, Abraham RG, Johnson KS, Mugica V, Molina MJ, Laskin A, Prather KA (2008) Characterization of Aerosols Containing Zn, Pb and Cl from an Industrial Region of Mexico City. Environ Sci Technol 42:7091–7097
Murphy DM, Hudson PK, Cziczo DJ, Gallavardin S, Froyd KD, Johnston MV, Middlebrook AM, Reinard MS, Thomson DS, Thornberry T, Wexler AS (2007) Distribution of lead in single atmospheric particles. Atmos Chem Phys 7:3195–3210
Ondov JM, Wexler AS (1998) Where do particulate toxins reside? An improved paradigm for the structure and dynamics of the urban mid-Atlantic aerosol. Environ Sci Technol 32:2547–2555
Ondráček J, Schwarz J, Ždímal V, Andĕlová L, Vodička P, Bízek V, Tsai C-J, Chen S-C, Smolík J (2011) Contribution of the road traffic to air pollution in the Prague city (busy speedway and suburban crossroads). Atmos Environ 45:5090–5100
Pacyna JM (1998) Source inventories for atmospheric trace metals. In: Harrison RM, van Grieken RE (eds) Atmospheric particles, IUPAC series on analytical and physical chemistry of environmental systems, vol 5. Wiley, Chichester, pp 385–423
Pan Y, Wang Y, Sun Y, Tian S, Cheng M (2013) Size-resolved aerosol trace elements at a rural mountainous site in Northern China: importance of regional transport. Sci Total Environ 461–462:761–771
Pietrodangelo A, Salzano R, Rantica E, Perrino C (2013) Characterisation of the local topsoil contribution to airborne particulate matter in the area of Rome (Italy). Atmos Environ 69:1–14
Pikridas M, Tasoglou A, Florou K, Pandis SN (2013) Characterization of the origin of fine particulate matter in a medium size urban area in the Mediterranean. Atmos Environ 80:264–274
Pio C, Mirante F, Oliveira C, Matos M, Caseiro A, Oliveira C, Querol X, Alves C, Martins N, Cerqueira M, Camões F, Silva H, Plana F (2013) Size segregated chemical composition of aerosol emissions in an urban road tunnel in Portugal. Atmos Environ 71:15–25
Public Utility Company Beogradske elektrane, www.beoelektrane.rs
Reponen T, Grinshpun SA, Trakumas S, Martuzevicius D, Wang ZM, LeMasters G, Lockey JE, Biswas P (2003) Concentration gradient patterns of aerosol particles near interstate highways in the Greater Cincinnati airshed. J Environ Monit 5:557–562
Salma I, Maenhaut W, Zemplén-Papp É, Záray G (2001) Comprehensive characterisation of atmospheric aerosols in Budapest, Hungary: physicochemical properties of inorganic species. Atmos Environ 35:4367–4378
Seinfeld JH, Pandis SN (1998) Atmospheric chemistry and physics: from air pollution to climate change. Wiley, New York
Song F, Gao Y (2011) Size distributions of trace elements associated with ambient particular matter in the affinity of a major highway in the New Jersey—New York metropolitan area. Atmos Environ 45:6714–6723
Stortini AM, Freda A, Cesari D, Cairns WRL, Contini D, Barbante C, Prodi F, Cescon P, Gambaro A (2009) An evaluation of the PM2.5 trace elemental composition in the Venice lagoon area and an analysis of the possible sources. Atmos Environ 43:6296–6304
Suarez AE, Ondov JM (2002) Ambient aerosol concentrations of elements resolved by size and by source: contributions of some cytokine-active metals from coal- and oil-fired power plants. Energy Fuel 16:562–568
Tsitouridou R, Papazova P, Simeonova P, Simeonov V (2013) Chemical and statistical interpretation of sized aerosol particles collected at an urban site in Thessaloniki, Greece. J Environ Sci Health A Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 48(14):1815–1828
Witt MLI, Meheran N, Mather TA, de Hoog JCM, Pyle DM (2010) Aerosols trace metals, particle morphology and total gaseous mercury in the atmosphere of Oxford, UK. Atmos Environ 44:1524–1538
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Ma W, Fu W, Yang X, Li C, Zhou B, Yu Q, Chen L (2013) Characteristics and ship traffic source identification of air pollutants in China-s largest port. Atmos Environ 64:277–286
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the INTERREG/CARDS-PHARE Adriatic New Neighbourhood Programme—Grant No. 06SER02/01/04. The authors are grateful to the Delegation of the European Union to Serbia. The authors were also grateful to the Ministry of education, Science and Technological Development which further supported financially this research within the projects 172001 and 43007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lammel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Đorđević, D., Stortini, A.M., Relić, D. et al. Trace elements in size-segregated urban aerosol in relation to the anthropogenic emission sources and the resuspension. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 10949–10959 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2998-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2998-1