Abstract
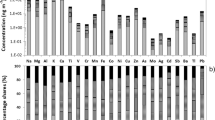
The results presented in this work demonstrate for the first time a distribution of elements in the spectral analysis of aerosols in the suburban continental Balkan Peninsula. Samples were collected in the suburban area of Belgrade (Serbia) in the period from March 2012 till December 2013. Results presented here are from long-term measurements of masses of size-segregated aerosols and macro- and microelements in the range of PM0.27–16. The following elements were analyzed: Al, Ag, As, Ba, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, Ni, Pb, Sb, Ti, Tl, V, and Zn; levels of Be, Hg, and Se were under the detection limits in all samples. Average concentrations and time and seasonal variations of particulate matter (PM) as well as element contents and their percentage shares are given. The results showed the domination of particle content around the accumulation mode in the range of 0.53 < Dp < 1.06 μm, but the fractional distribution of elements showed maximal average concentrations in different fractions depending on the origin of each element. Crustal elements (Al, Ca, Fe, Mg, Mn, Ti, etc.) dominated in coarse mode, while anthropogenic elements (As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Sb, etc.) were mainly distributed in fine mode fractions. Some elements, such are As and Ni, were detected in investigated aerosols only occasionally, while others, such as Ca, Fe, and Mg, were detected in all analyzed samples. The application of multivariate analysis (PCA) demonstrated the connection between the elements of similar origin, in fine fractions mainly of anthropogenic origin, while in coarse mode of crustal origin, indicating the resuspension with contribution of about 40%. The contents of some measured elements were compared with their contents in aerosols in some European suburban areas.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Abdi H, Williams LJ (2010) Principal component analysis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev : Comput Stat, 1 7 2(4):433–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/wics.101
Albrecht BA (1989) Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science (80-. ) 245:1227–1230. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.245.4923.1227
Allard P, Aiuppa A, Loyer H, Carrot F, Gaudry A, Pinte G, Michel A, Dongarrà G (2000) Acid gas and metal emission rates during long-lived basalt degassing at Stromboli Volcano. Geophys Res Lett, 15 4 27(8):1207–1210. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999GL008413
Bagnato E et al (2011) Leachate analyses of volcanic ashes from Stromboli volcano: a proxy for the volcanic gas plume composition? J Geophys Res, 14 9 116(D17):D17204. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015512
Berner A (1972) Praktische Erfahrungen mit einem 20-Stufen-Impactor. Staub – Reinhalt Luft 32:315
Calabrese S, Aiuppa A, Allard P, Bagnato E, Bellomo S, Brusca L, D’Alessandro W, Parello F (2011) Atmospheric sources and sinks of volcanogenic elements in a basaltic volcano (Etna, Italy). Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1 12 75(23):7401–7425. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GCA.2011.09.040
Castillo S, Moreno T, Querol X, Alastuey A, Cuevas E, Herrmann L, Mounkaila M, Gibbons W (2008) Trace element variation in size-fractionated African desert dusts. J Arid Environ, 1 6 72(6):1034–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JARIDENV.2007.12.007
Charlson RJ, Schwartz SE, Hales JM, Cess RD, Coakley JA, Hansen JE, Hofmann DJ (1992) Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science (80-. ) 255:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.255.5043.423
Christoforidis A, Stamatis N (2009) Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma 151:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.04.016
Contini D, Belosi F, Gambaro A, Cesari D, Stortini AM, Bove MC (2012) Comparison of PM10 concentrations and metal content in three different sites of the Venice Lagoon: an analysis of possible aerosol sources. J Environ Sci 24:1954–1965. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)61027-9
Dongarrà G, Manno E, Varrica D, Vultaggio M (2007) Mass levels, crustal component and trace elements in PM 10 in Palermo, Italy. Atmos Environ 41:7977–7986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.015
Đorđević D, Mihajlidi-Zelić A, Relić D, Lj I, Huremović J, Stortini AM, Gambaro A (2012) Size-segregated mass concentration and water soluble inorganic ions in an urban aerosol of the Central Balkans (Belgrade). Atmos Environ 46:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2011.09.057
Đorđević D, Stortini AM, Relić D, Mihajlidi-Zelić A, Huremović J, Barbante C, Gambaro A (2014) Trace elements in size-segregated urban aerosol in relation to the anthropogenic emission sources and the resuspension. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10949–10959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2998-1
Đorđević D, Buha J, Stortini AM, Mihajlidi-Zelić A, Relić D, Barbante C, Gambaro A (2016) Mass distributions and morphological and chemical characterization of urban aerosols in the continental Balkan area (Belgrade). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:851–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5271-3
Fernández Álvarez F, Ternero Rodríguez M, Fernández Espinosa AJ, Gutiérrez Dabán A (2004) Physical speciation of arsenic, mercury, lead, cadmium and nickel in inhalable atmospheric particles. Anal Chim Acta 524:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.02.004
Formenti, P. et al., 2003. Chemical composition of mineral dust aerosol during the Saharan Dust Experiment (SHADE) airborne campaign in the Cape Verde region, September 2000. J Geophys Res, 27 9, 108(D18), p. 8576. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002648
Government, U.S. (2010) eCFR—Code of Federal Regulations, Electronic Code of Federal Regulations
Hieu NT, Lee B-K (2010) Characteristics of particulate matter and metals in the ambient air from a residential area in the largest industrial city in Korea. Atmos Res, 1 11 98(2–4):526–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2010.08.019
Hueglin C, Gehrig R, Baltensperger U, Gysel M, Monn C, Vonmont H (2005) Chemical characterisation of PM2.5, PM10 and coarse particles at urban, near-city and rural sites in Switzerland. Atmos Environ 39:637–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.10.027
Isley CF, Nelson PF, Taylor MP, Stelcer E, Atanacio AJ, Cohen DD, Mani FS, Maata M (2018) Reducing mortality risk by targeting specific air pollution sources: Suva, Fiji. Sci Total Environ 612:450–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.225
Jamieson RA, Baldini JU, Frappier AB, Müller W (2015) Volcanic ash fall events identified using principal component analysis of a high-resolution speleothem trace element dataset. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 15 9 426:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EPSL.2015.06.014
Jiang SY, Kaul DS, Yang F, Sun L, Ning Z (2015) Source apportionment and water solubility of metals in size segregated particles in urban environments. Sci Total Environ 533:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.146
Johansson C, Norman M, Burman L (2009) Road traffic emission factors for heavy metals. Atmos Environ 43:4681–4688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.10.024
Kampa M, Castanas E (2008) Human health effects of air pollution. Environ Pollut 151:362–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.012
Karanasiou A, Sitaras I, Siskos P, Eleftheriadis K (2007) Size distribution and sources of trace metals and n-alkanes in the Athens urban aerosol during summer. Atmos Environ, 1 4 41(11):2368–2381. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2006.11.006
Kumar M, Furumai H, Kurisu F, Kasuga I (2010) Evaluating the mobile heavy metal pool in soakaway sediment, road dust and soil through sequential extraction and isotopic exchange. Water Sci Technol 62:920–928. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2010.911
Lawrence CR, Neff JC (2009) The contemporary physical and chemical flux of aeolian dust: a synthesis of direct measurements of dust deposition. Chem Geol 267:46–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.02.005
Li X, Wang L, Wang Y, Wen T, Yang Y, Zhao Y, Wang Y (2012) Chemical composition and size distribution of airborne particulate matters in Beijing during the 2008 Olympics. Atmos Environ 50:278–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.12.021
Lü S, Zhang R, Yao Z, Yi F, Ren J, Wu M, Feng M, Wang Q (2012) Size distribution of chemical elements and their source apportionment in ambient coarse, fine, and ultrafine particles in Shanghai urban summer atmosphere. J Environ Sci (China) 24:882–890
Masiol M, Squizzato S, Ceccato D, Pavoni B (2015) The size distribution of chemical elements of atmospheric aerosol at a semi-rural coastal site in Venice (Italy). Role Atmos Circ Chemosphere 119:400–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.06.086
Mbengue S, Alleman LY, Flament P (2014) Size-distributed metallic elements in submicronic and ultrafine atmospheric particles from urban and industrial areas in northern France. Atmos Res 135:35–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.08.010
Mihajlidi-Zelić, A. et al. (2014) Water-soluble inorganic ions in urban aerosols of the continental part of Balkans (Belgrade) during the summer – autumn (2008). Open Chem, 1 1.13(1). doi: 10.1515/chem-2015-0010
Miranda J, Crespo I, Morales MA (2000) Absolute principal component analysis of atmospheric aerosols in Mexico city. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 29 3 7(1):14–18. https://doi.org/10.1065/espr199910.006
Moreno T, Querol X, Alastuey A, Viana M, Salvador P, Sánchez de la Campa A, Artiñano B, de la Rosa J, Gibbons W (2006) Variations in atmospheric PM trace metal content in Spanish towns: illustrating the chemical complexity of the inorganic urban aerosol cocktail. Atmos Environ 40:6791–6803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.074
Nriagu JO (1989) A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature 338:47–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/338047a0
Pakkanen TA, Loukkola K, Korhonen CH, Aurela M, Mäkelä T, Hillamo RE, Aarnio P, Koskentalo T, Kousa A, Maenhaut W (2001) Sources and chemical composition of atmospheric fine and coarse particles in the Helsinki area. Atmos Environ 35:5381–5391. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00307-7
Pan Y, Wang Y, Sun Y, Tian S, Cheng M (2013) Size-resolved aerosol trace elements at a rural mountainous site in Northern China: importance of regional transport. Sci Total Environ 461–462:761–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.04.065
Pennanen AS, Sillanpää M, Hillamo R, Quass U, John AC, Branis M, Hůnová I, Meliefste K, Janssen NAH, Koskentalo T, Castaño-Vinyals G, Bouso L, Chalbot M-C, Kavouras IG, Salonen RO (2007) Performance of a high-volume cascade impactor in six European urban environments: mass measurement and chemical characterization of size-segregated particulate samples. Sci Total Environ 374:297–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.002
Poikolainen J, Kubin E, Piispanen J, Karhu J (2004) Atmospheric heavy metal deposition in Finland during 1985–2000 using mosses as bioindicators. Sci Total Environ 318:171–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00396-6
Popovic A, Djordjevic D, Polic P (2001) Trace and major element pollution originating from coal ash suspension and transport processes. Environ Int, 1 4 26(4):251–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(00)00114-8
Popovic A, Djordjevic D (2009) pH-dependent leaching of dump coal ash—retrospective environmental analysis. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery Utilization Environ Effects, 9 10 31(17):1553–1560. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567030802094003
Popovic A, Djordjevic D (2015a) Trace and major elements in ash of “Nikola Tesla A” power plant dump (I)—leached concentrations and environmental implications. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery Utilization Environ Effects, 3 6 37(11):1224–1232. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2011.606872
Popovic A, Djordjevic D (2015b) Trace and major elements in ash of “Nikola Tesla A” power plant dump (II)-associations of elements in active cassette ash. Energy Sources Part A: Recovery Utilization Environ Effects, 18 6 37(12):1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2011.615804
Sarigiannis DΑ, Karakitsios SP, Kermenidou M, Nikolaki S, Zikopoulos D, Semelidis S, Papagiannakis A, Tzimou R (2014) Total exposure to airborne particulate matter in cities: the effect of biomass combustion. Sci Total Environ 493:795–805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.055
Sarigiannis DΑ, Karakitsios SP, Zikopoulos D, Nikolaki S, Kermenidou M (2015) Lung cancer risk from PAHs emitted from biomass combustion. Environ Res 137:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2014.12.009
Schaumann F, Borm PJA, Herbrich A, Knoch J, Pitz M, Schins RPF, Luettig B, Hohlfeld JM, Heinrich J, Krug N (2004) Metal-rich ambient particles (particulate matter 2.5) cause airway inflammation in healthy subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:898–903. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200403-423OC
Serbula SM, Miljkovic DD, Kovacevic RM, Ilic AA (2012) Assessment of airborne heavy metal pollution using plant parts and topsoil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 76:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.10.009
Song F, Gao Y (2011) Size distributions of trace elements associated with ambient particular matter in the affinity of a major highway in the New Jersey–New York metropolitan area. Atmos Environ 45:6714–6723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.08.031
Sun J, Zhang Q, Canagaratna MR, Zhang Y, Ng NL, Sun Y, Jayne JT, Zhang X, Zhang X, Worsnop DR (2010) Highly time- and size-resolved characterization of submicron aerosol particles in Beijing using an Aerodyne Aerosol Mass Spectrometer. Atmos Environ 44:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.03.020
Wang H-C, John W (1988) Characteristics of the Berner impactor for sampling inorganic ions. Aerosol Sci Technol 8:157–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786828808959179
Wang J, Nakazato T, Sakanishi K, Yamada O, Tao H, Saito I (2004) Microwave digestion with HNO3/H2O2mixture at high temperatures for determination of trace elements in coal by ICP-OES and ICP-MS. Anal Chim Acta 514:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.03.040
Wang ZZ, Deguchi Y, Kuwahara M, Taira T, Zhang XB, Yan JJ, Liu JP, Watanabe H, Kurose R (2013) Quantitative elemental detection of size-segregated particles using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta B At Spectrosc 87:130–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2013.05.034
Zhang W, Zhuang G, Guo J, Xu D, Wang W, Baumgardner D, Wu Z, Yang W (2010) Sources of aerosol as determined from elemental composition and size distributions in Beijing. Atmos Res, 1 2 95(2–3):197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSRES.2009.09.017
Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Q, Liang Z (2010) Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast of China. Sci Total Environ 408:726–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.075
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, within the project ON172001. The authors are also grateful to the Delegation of the European Union to Serbia: INTERREG/CARDS-PHARE Adriatic New Neighborhood Programme—grant no. 06SER02/01/04.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lammel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Đuričić-Milanković, J., Anđelković, I., Pantelić, A. et al. Partitioning of particulate matter and elements of suburban continental aerosols between fine and coarse modes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 20841–20853 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2037-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2037-8