Abstract
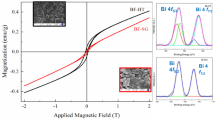
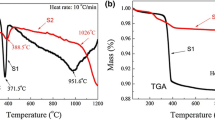
Gel fibres of barium M ferrite, BaFe12O19, were blow spun from an aqueous inorganic sol and calcined at temperatures up to 1200°C. The ceramic fibres were shown by X-ray diffraction to be single phase crystalline M ferrite at 1000°C, and surface area and porosity measurements indicated an unusually high degree of sintering at this temperature. The fibres also demonstrated a favourable grain structure of less than 0.1 μm at this temperature and maintained a small grain size of less than 4 μm even up to 1200°C, an important factor in the magnetic properties of this material.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
V. Adelskold, Arkiv. Kemi., Min. Geol. 12A (1938) 1.
G. H. Jonker, H.P. Wijn and P. B. Braun, Phil. Techn. Rev. 18 (1956) 145.
J. J. Went, G. W. Rathenau, E. W. Gorter and G. W. van Oosterhaut, Phil. Techn. Rev. 13 (1952) 194.
E. A. M. van der Broek and A. L. Stuijts, Ibid 37 (1977-8) 169.
H. Stablein, in “Ferromagnetic Materials” Vol. 3, edited by E. P Wohlfarth (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982) p. 448.
E. E. Riches, in “Ferrites” (Mills and Boon Technical Library, London, 1972) p. 10.
W. H. von Aulock and C. E. Fay, in “Linear Ferrite Devices for Microwave Applications” (Academic Press, New York, 1968).
E. E. Riches, in “Ferrites” (Mills and Boon Technical Library, London, 1972) p. 37.
H. Stablein, in “Ferromagnetic Materials” Vol. 3, edited by E. P Wohlfarth (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982) pp. 462535.
H. Haneda, Ch. Miyakawa and H. Kojima, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 57 (1974) 354.
H. G. Richter, IEEE Trans., MAG-4 (1968) 263.
K. Haneda and H. Kojima, J. Appl. Phys. 44 (1973) 3760.
R. L. Coble, J. Appl. Phys. 32 (1961) 787.
A. Kelly, in “Strong Solids” (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1973).
D. K. Hale, J. Mater. Sci. 11 (1976) 2105.
H. A. Goldberg, US Pat. 4725 490 (1973).
M. J. Morton, J. D. Birchall and J. E. Cassidy, UK Pat. 1360 200 (1974).
H. Stablein, Tech. Mitt. Krupp., Forsch.-Ber. 26 (1968) 81.
J. Smit and H. P. J. Wijn, in “Ferrites” (Philips Technical Library, Eindhoven, 1959) p. 221.
A. G. Sadler, J. Can. Ceram. Soc. 34 (1965) 155.
M. Erchak, I. Fankuchen and R. Ward, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc. 68 (1946) 2085 and 2093.
H. Stablein, in “Ferromagnetic Materials” Vol. 3, edited by E. P Wohlfarth (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1982) pp. 5057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PULLAR, R.C., TAYLOR, M.D. & BHATTACHARYA, A.K. Novel aqueous sol–gel preparation and characterization of barium M ferrite, BaFe12O19 fibres. Journal of Materials Science 32, 349–352 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018593014378
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018593014378